According to the description of the working principle and clinical mechanism of IPL, the intense pulsed light therapy device can be used to treat vascular skin diseases and superficial pigmentary skin diseases, reduce hair, and treat mild to moderate inflammatory acne (acne vulgaris). Based on the theory of selective photothermal action and its extended theory, strong pulsed light can cause vascular occlusion in lesions, thereby treating vascular skin diseases. This article will summarize the relevant application experience in clinical practice.
Medical Aesthetics Academic Circle | IPL Working Principle and Clinical Mechanism of Action "," Medical Aesthetics Academic Circle | IPL Working Principle and Clinical Mechanism of Action "," Phototherapy Miracle Egg | Identifial Flash Intense Pulse Light Therapy Device, Reshaping Your Eggshell Muscle with Technology "Click on the blue text to read ←
1、 The dose-response relationship of strong pulsed light
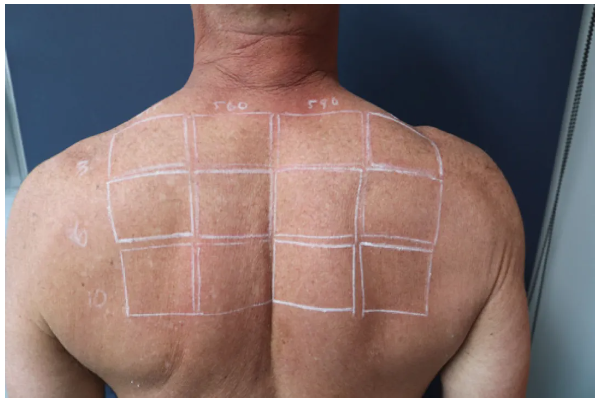
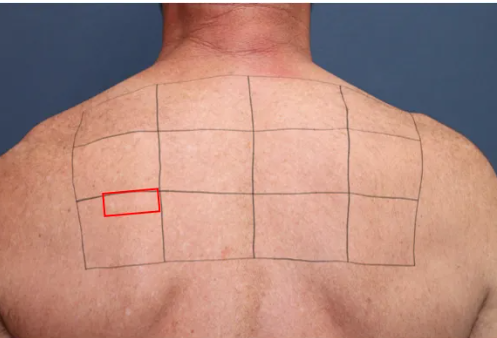
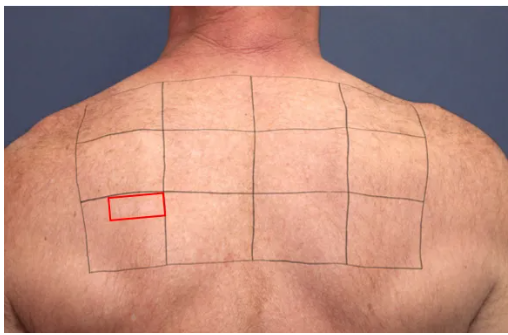
Michael B. Lipp et al. [1] used a marker pen to mark a 4 × 3 grid on the skin surface of type III skin subjects, and selected different combinations of filters (515nm, 560nm, 590nm, 530-650nm&900-1200nm), energy density, pulse width, and number of sub pulses. A single irradiation was applied to the skin surface to compare the effects of different pulse light parameters on the skin.
Science Popularization · Truth Faction | Key Terminology Explanation of Intense Pulsed Light 11: Filter "," Science Popularization · Truth Faction | Key Terminology Explanation of Intense Pulsed Light 8: Energy Density "," Science Popularization · Truth Faction | Key Terminology Explanation of Intense Pulsed Light 2: Pulse Width and Pulse Frequency "Click on the blue text to read ←
Follow up photos were taken at baseline, immediately after surgery, 4 hours after surgery, 24 hours after surgery, 1 week after surgery, 2 weeks after surgery, and 4 weeks after surgery.
[Figure. Baseline period]
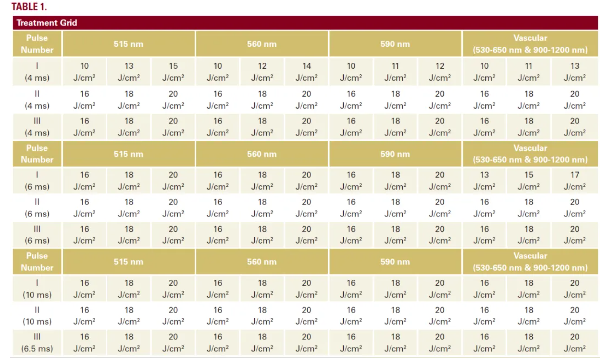
It can be observed that the immediate postoperative erythema becomes more pronounced with an increase in energy density, an increase in spectral range, a decrease in the number of sub pulses, and a decrease in pulse width. However, in terms of pulse width, the 515nm filter is an exception, and it is observed that its response becomes more pronounced as the pulse width increases. Compared with the 590nm filter, the erythema response of the vascular filter is relatively stronger, and the 590nm filter is comparable to the 560nm filter. At the same time as the erythema becomes more pronounced, freckle like nevi become slightly darker.
Immediately after surgery, using a 515nm filter, higher energy density, and longer pulses will observe more pronounced tissue reactions
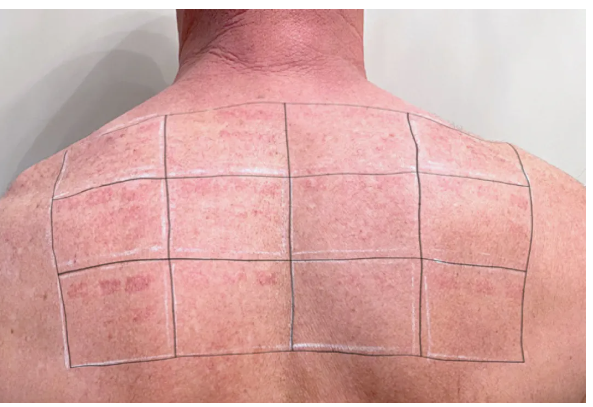
The photo taken 4 hours after surgery showed the same overall trend as immediately after surgery. However, the erythema is generally more pronounced and darker in color. The freckle like mole can still be seen darkening in the treatment area, accompanied by obvious erythema.
[Image. 4 hours after surgery]
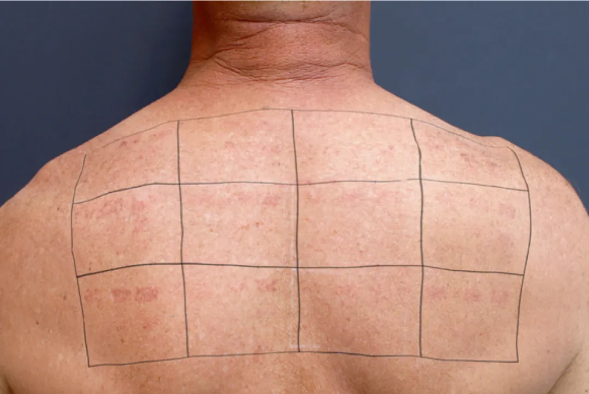
The follow-up photos taken 24 hours after surgery also followed the same overall trend, but the erythema improved. In addition, the characteristic of erythema is more reddish brown tones. Freckle like nevi and pigmentation also become lighter.
[Image. Improvement of erythema 24 hours after surgery]
The erythema further subsided one week after surgery. A small amount of scabbing was observed in the single pulse treatment area with all energy densities and pulse widths of the 515nm filter, as well as in the single pulse treatment area with an energy density of 20J/cm ² of the 560nm filter. The degree of scab formation is consistent with the degree of immediate postoperative erythema.
One week after surgery, superficial scabs appeared in some treatment areas
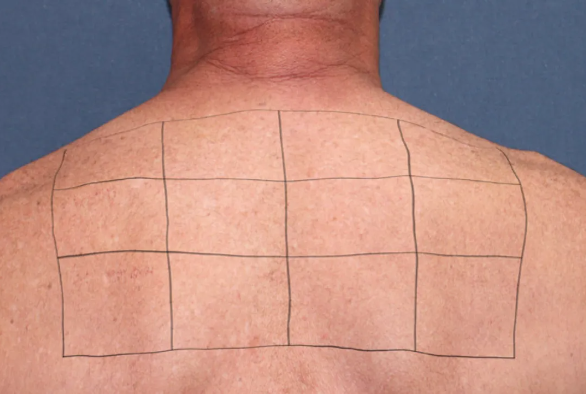
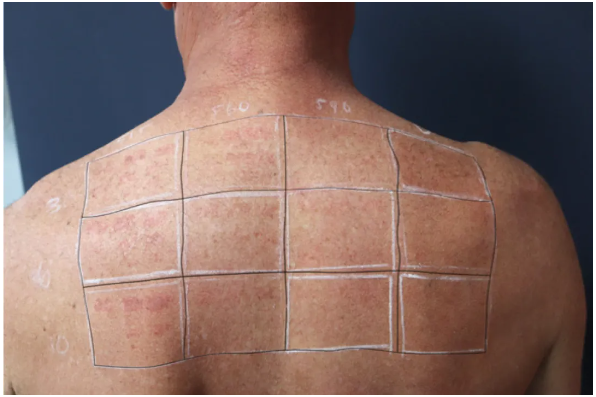
At the 2-week follow-up, all scabs had healed. Although most of the scabbed areas have no sequelae, some scabbed areas (515nm, single pulse, 10ms pulse width, energy density of 18 and 20J/cm ²) exhibit well-defined square patches of depigmented hairlessness. During the 4-week follow-up, these two plaques became clearer.
Two weeks after surgery, superficial scabs disappear, and areas with hairlessness and reduced pigmentation appear
Four weeks after surgery, the area of hypopigmentation becomes clearer
The results of this case study are consistent with the theory of intense pulsed light therapy. The postoperative erythema is inversely proportional to the wavelength of the filter (for example, the erythema of the 515nm filter is the strongest, while the erythema of the 590nm filter is the weakest). Given that strong pulsed light devices can filter out wavelengths shorter than the selected filter, the 515nm filter will allow for a larger wavelength spectrum to target tissue chromophores with higher absorption coefficients. In addition, the 515nm filter targets oxygenated hemoglobin on all major (i.e. 540nm and 577nm) and minor (i.e. 920-940nm) absorption peaks. Finally, it targets water within the infrared wavelength range. By targeting melanin, oxygenated/deoxygenated hemoglobin, and water, intense pulsed light can treat pigmentary lesions, vascular lesions, and stimulate collagen remodeling. The 560nm filter did not produce a strong erythema reaction, possibly because it did not target the 540nm oxygenated hemoglobin absorption peak. The vascular filter has a similar erythema response to the 560nm filter, possibly because it targets the same oxygenated hemoglobin peak. The 590nm filter has the weakest erythema response, possibly because it did not capture the 540 and 577nm oxygenated hemoglobin peaks. The slight darkening of freckle like nevi is associated with a stronger erythema response, which can be explained by the fact that shorter wavelengths allow for better targeting of melanin with higher absorption coefficients.
Red rash reactions were also observed at higher energy densities and longer pulse widths. Transmitting greater energy and interacting with tissue chromophores will result in stronger reactions. In addition, a longer pulse width helps to have a longer interaction time with the target chromophore. The fewer sub pulses, the stronger the erythema reaction. On the contrary, distributing a certain energy density to multiple sub pulses can use lower energy for each sub pulse, keeping tissue reactions to a minimum. This causes the surrounding tissue to cool down, while the target chromophore heats up sequentially.
Therefore, in the treatment of intense pulsed light, various factors such as indications and skin types should be comprehensively considered, and a more suitable combination of parameters such as filter, energy density, pulse width, and number of sub pulses should be selected to improve the treatment effect and reduce damage to surrounding normal tissues.
2、 Treatment of rosacea with intense pulsed light
Jiachen Yuan et al. [2] studied the therapeutic effect of adjustable square wave intense pulsed light on erythematous telangiectatic rosacea (ETR) through animal experiments and clinical cases.
Firstly, LL-37 was used to induce an ETR model in the back of mice, which were divided into a blank control group, LL-37 group, and AOPT-LTL group, with 5 mice in each group. The blank group did not receive any treatment, the LL-37 group did not receive any treatment after establishing the ETR model, and the AOPT-LTL group was treated with adjustable square wave intense pulsed light. The treatment parameters are set as follows: 590nm filter, 10J/cm ² energy density, three sub pulses, with sub pulse widths of 8ms, 6ms, and 6ms, and sub pulse intervals of 35ms. A total of three treatments are administered with 24-hour intervals. After treatment, the results of dermatoscopy showed that intense pulsed light irradiation can significantly improve the erythema at the lesion site, reduce capillary density, and significantly improve the score. HE staining showed that after injection of LL-37, mouse capillaries proliferated and expanded, accompanied by significant inflammatory cell infiltration; The use of intense pulsed light irradiation therapy can significantly improve tissue inflammation infiltration and vascular abnormalities.
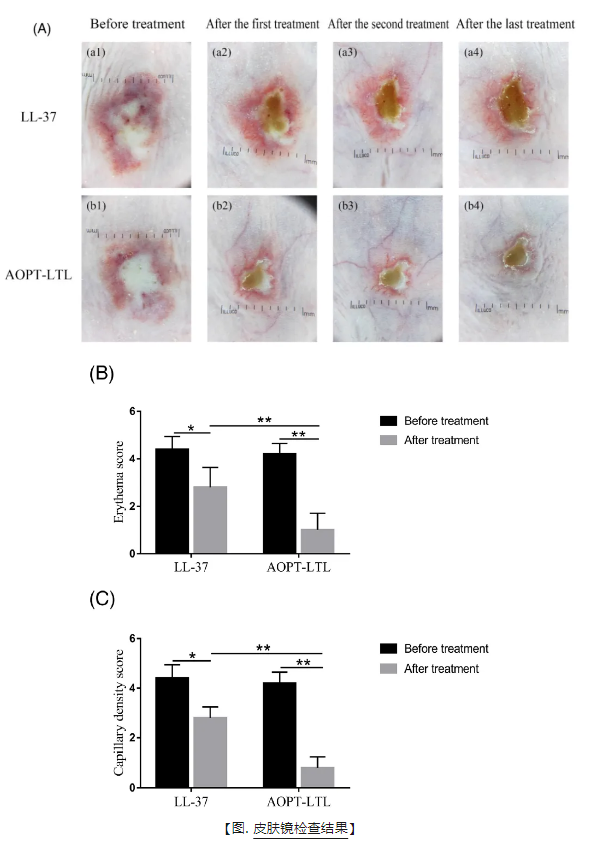
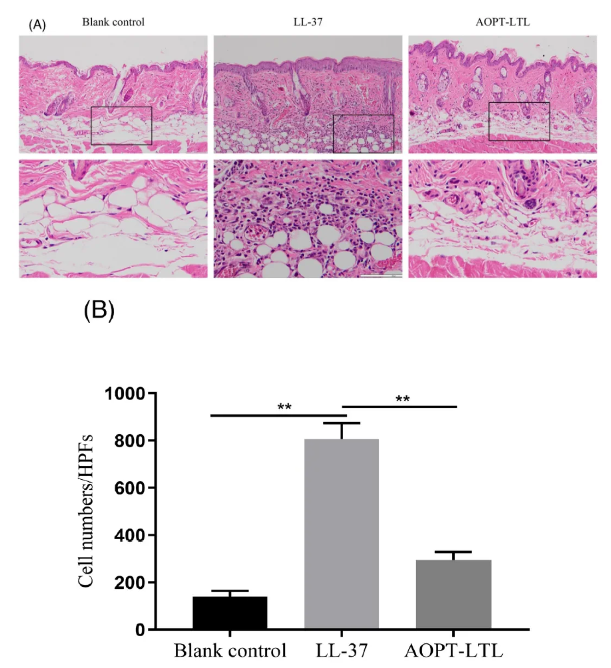
【 Figure. HE staining histological examination results 】
In terms of clinical application, 23 ETR subjects were recruited and treated with adjustable square wave intense pulsed light, 590/640nm filter, energy density range of 10-16J/cm ², three sub pulse output modes with sub pulse widths of 8, 6, and 6ms, sub pulse intervals of 35-40ms, treatment frequency of 6-10 times, and interval of 2 weeks.
Collect facial images of subjects using VISIA and perform GFSS and CEA scoring. One week after surgery, the VISIA red zone score decreased by 22.17, GFSS score decreased by 5.3, and CEA score decreased by 1.75; Three months after surgery, the VISIA red zone score decreased by 17.5, GFSS score decreased by 4.24, and CEA score decreased by 1.43; The above score reductions showed significant differences compared to the baseline period. During the treatment process, some subjects experienced transient erythema, which resolved spontaneously within 1-2 days without long-term adverse reactions such as pigmentation changes, edema, blisters, etc.
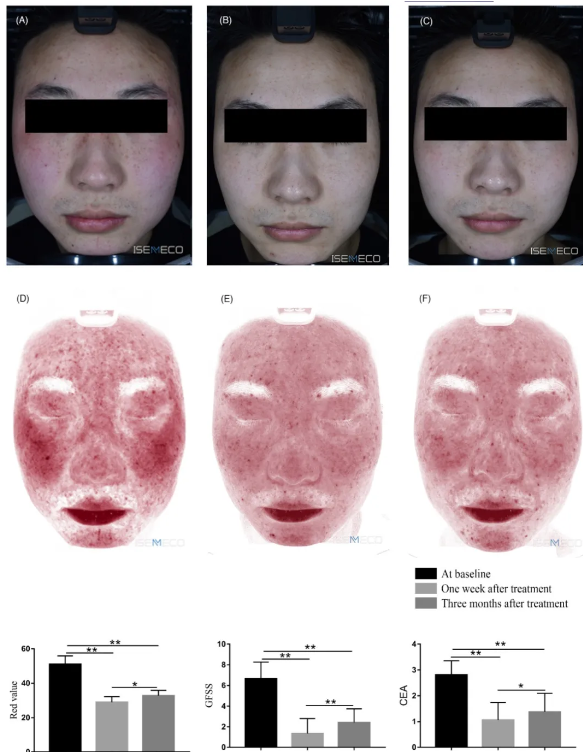
[Image. VISIA Inspection Results]
From this study, it can be seen that using an adjustable square wave strong pulse light therapy device for the treatment of erythematous telangiectasia type rosacea has good effectiveness and safety.
3、 Intense pulsed light therapy for facial capillary dilation
Pan Hu et al. [3] studied the clinical application of polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) combined with intense pulsed light in the treatment of facial telangiectasia. This study recruited 40 subjects with facial capillary dilation and randomly divided them into two groups: the IPL group treated with intense pulsed light alone and the combination group treated with PDRN combined with intense pulsed light, with 20 subjects in each group.
The parameters for intense pulsed light therapy in the IPL group are set as vascular vascular filter, twin pulse output, sub pulse width of 5ms, sub pulse interval of 50ms, and energy density of 15-20J/cm ²; The parameters of the combined group's intense pulsed light were consistent with those of the IPL group, and PDRN was applied using a rolling needle after intense pulsed light treatment. Both groups received two treatments with a one month interval between treatments, and VISIA image analysis was used as the evaluation index.
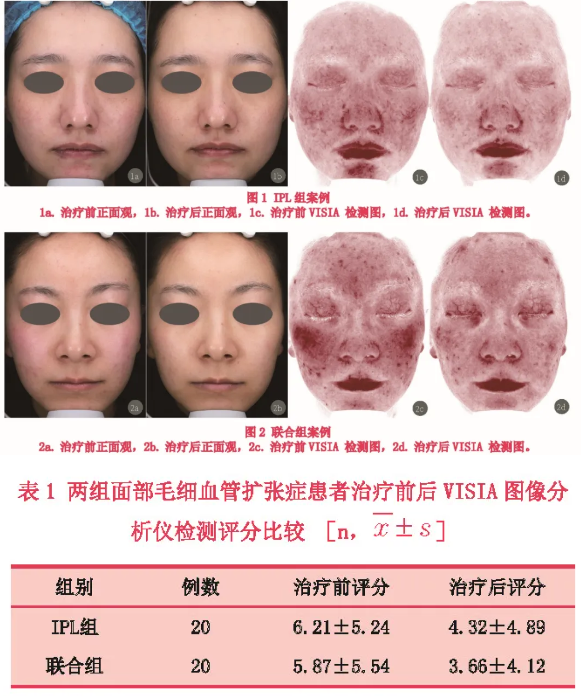
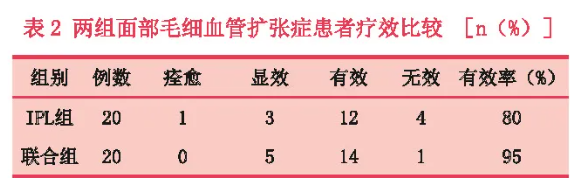
From the post-treatment scores and VISIA image analysis, it can be seen that using strong pulsed light alone to treat facial telangiectasia can achieve an 80% effective rate. If combined with PDRN, the treatment efficacy can be increased to 95%. There were no serious adverse reactions observed in either treatment group.
4、 Summary
The strong pulse light therapy device is based on the theory of selective photothermal action and its extended theory, which targets the heating of hemoglobin to promote vascular occlusion and achieve the goal of treating vascular skin diseases. During treatment, 560nm, 590nm, or specialized vascular filters with appropriate pulse width, number of sub pulses, energy density, and other parameters are usually selected based on the patient's skin type and lesion type, which have significant therapeutic effects.