Share:

In the continuous innovation of medical technology, cold air therapy devices have brought patients a new treatment experience with their unique treatment methods. This article will delve into the clinical application of cold air therapy devices.
1、 Definition of Low Temperature Therapy
Low temperature therapy is a method of using low temperature to act on diseased or damaged tissues, causing a temporary decrease in local or systemic temperature, thereby achieving analgesic, hemostatic, anti-inflammatory and other effects. Contact cooling is commonly used, such as ice compress and cold gel; Refrigerant spraying, such as liquid nitrogen and dry ice
2、 Cold air therapy device
By cooling and spraying air onto the treatment site of the patient, low-temperature stimulation can alleviate swelling, inflammation, muscle spasms, pain, contusions, and hematomas, as well as reduce metabolic rate and oxygen demand of surrounding tissues, thereby inhibiting the spread of injury to healthy areas, avoiding secondary damage, promoting tissue repair and wound healing. To achieve therapeutic effects. Widely used in the clinical medical field.
3、 The mechanism of action of cold air therapy
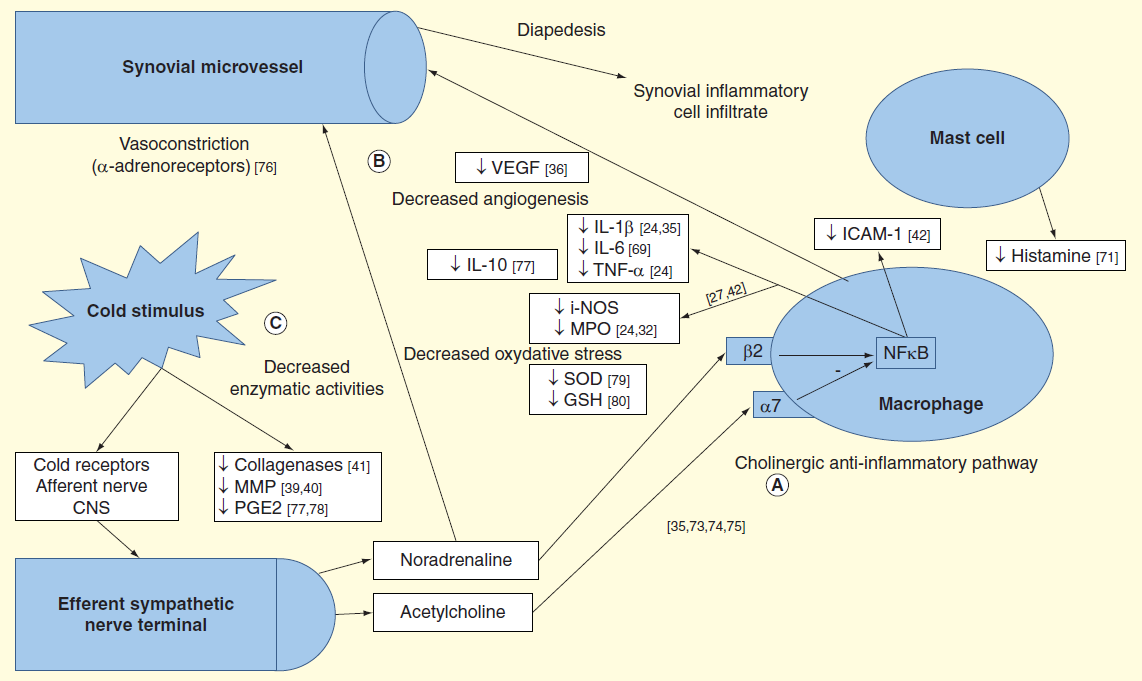
Xavier GuillotWaiting for someone[1]Summarizing the molecular mechanism of hypothermia therapy, inflammation promotes angiogenesis during the treatment process, which in turn benefits inflammatory cell infiltration and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway shown in Figure A, after cold stimulation, the autonomic nervous system is activated, and sympathetic neurons release acetylcholine that binds to a7nAchR receptors and noradrenaline that binds to β 2 adrenergic receptors. These ligand receptor interactions inhibit the NF κ B pathway, subsequently downregulating the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress agents, and adhesion molecule genes. In vasoconstriction pathway B, norepinephrine also induces vasoconstriction through alpha adrenergic receptors that bind to the vascular wall, which helps to limit inflammation. Low temperature therapy can also downregulate the expression of angiogenic factors such as VEGF. In enzyme pathway C, hypothermia therapy may also downregulate the activity of important enzymes involved in joint inflammation and destruction.
4、 Clinical application cases
Based on the mechanism of action of cold air low-temperature therapy, in clinical applications, cold air therapy can be used to alleviate pain and reduce postoperative adverse reactions such as redness, swelling, and inflammation during and after phototherapy or injection therapy on the skin
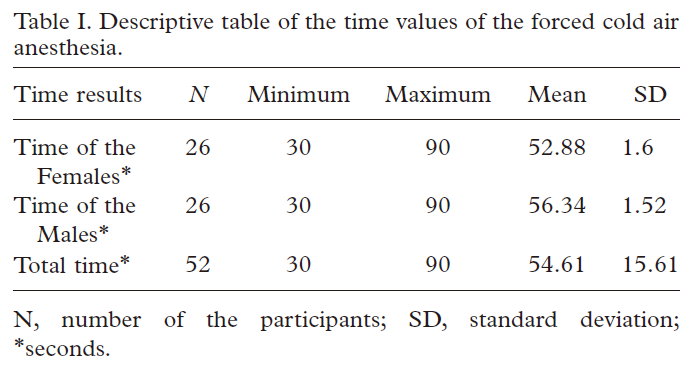
(1) Study on the onset time of anesthesia represented by cold air
The low temperature of cold air can significantly reduce the skin nerve conduction velocity by affecting the exchange between Ca2+and Na+in nerve cells. For every 1 ℃ decrease in skin temperature, the nerve conduction velocity will decrease by 0.4m/s.
(2) The application of cold air in laser therapy
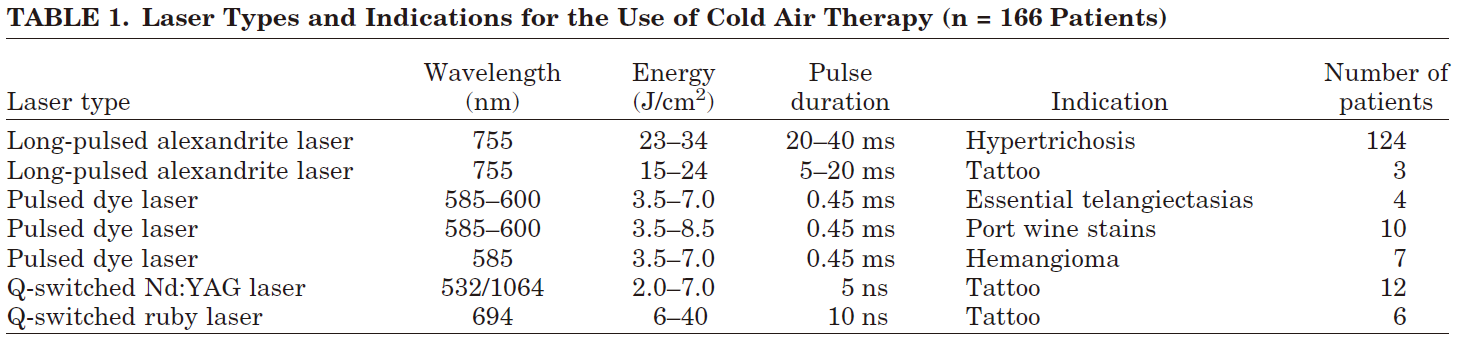
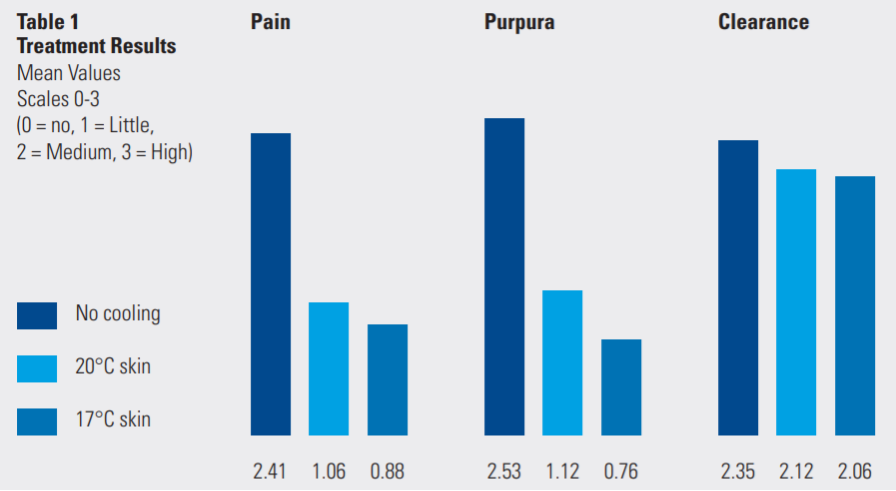
1. Christian Raulin et al. After comparison, 100% of the participants stated that they would prefer cold air as the method of facial skin cooling; Compared with gel, 63% of patients had shorter erythema duration, 74% of subjects had lower erythema degree, 70% had less purpura, and 83% had less scab after cooling with cold air; In addition, due to the reduction of pain and the decrease in the risk of epidermal thermal injury, the energy of laser treatment can be increased by 15% -30%. In this experiment, after blowing cold air at -15 ℃ for 8 seconds, the epidermal temperature can be reduced to 15 ℃, significantly reducing the pain of treatment and the incidence of adverse reactions. It can be used as an effective auxiliary method for skin laser therapy.
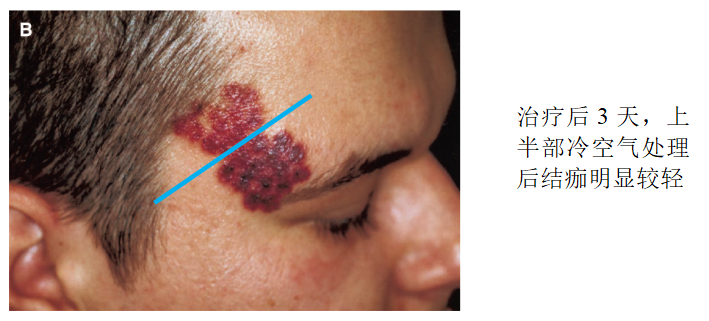
2.Baerbel GreveDuring the treatment of wine stains with pulsed dye laser, a comparison was made between cold air cooling and non cooling crack surfaces- After continuous cold air blowing at 15 ℃ for 8 seconds, the epidermal temperature drops to 15 ℃, and then pulse dye laser treatment is performed. The results showed that 9 patients (69%) felt that laser treatment accompanied by cold air significantly reduced pain, and the incidence of adverse reactions such as purpura, erythema, edema, hypopigmentation, pigmentation, scars, etc. in the cooling area was significantly reduced. Stefan Hammes et al. [6] also reached a similar conclusion that when using pulsed dye laser to treat facial telangiectasia, the use of cold air cooling significantly reduced pain scores and purpura scores, and the most suitable epidermal temperature was reduced to 20 ℃. On the basis of not significantly affecting the vascular treatment effect, it improved patient comfort and reduced the occurrence of adverse reactions.
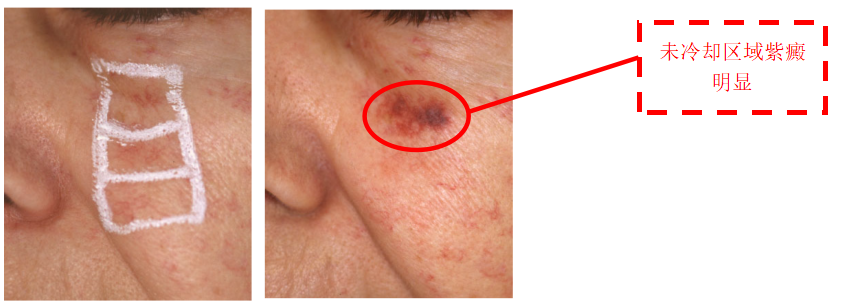
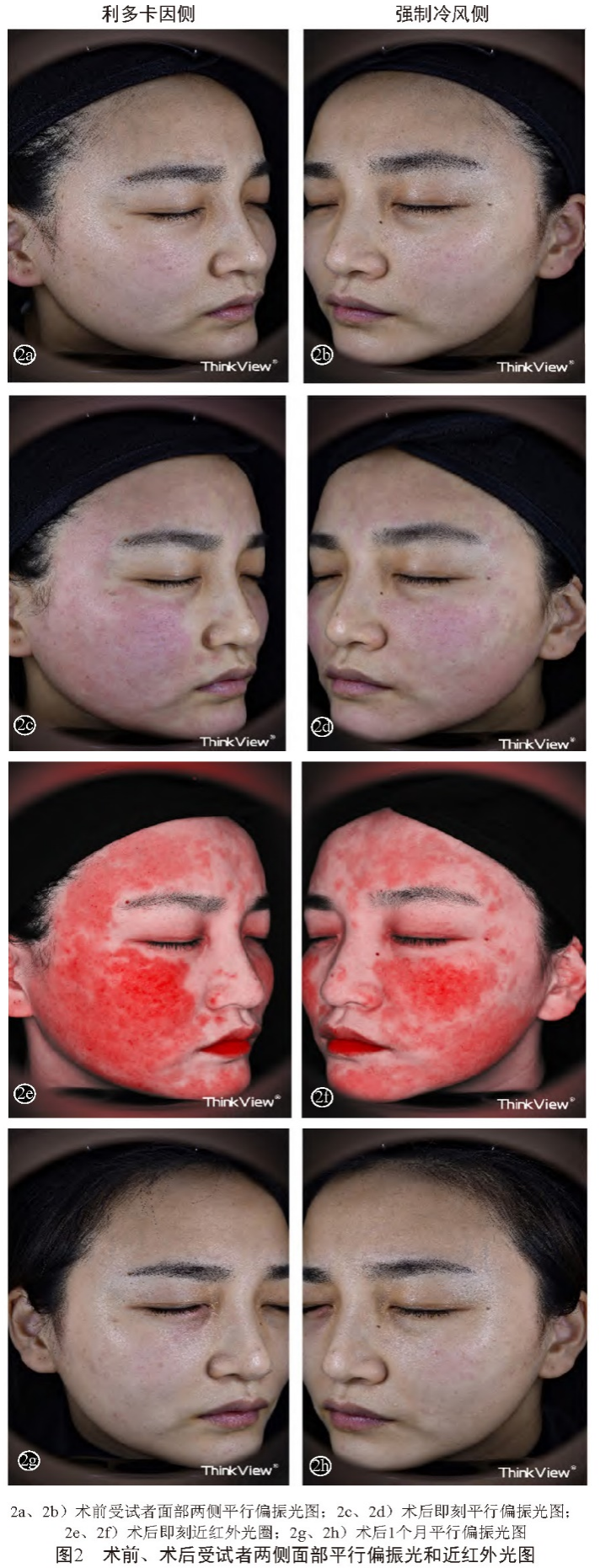
When treating facial photoaging with picosecond dot matrix laser, cold air can also be used in combination for pain relief, as confirmed by Zhou Chenxi et al. [7] through experiments. Before picosecond dot matrix laser treatment, lidocaine cream was applied to one side of the face, while cold air cooling was used on the other side. After laser treatment, the results showed that the epidermal temperature on the cold air cooling side was significantly lower than that on the contralateral lidocaine cream group during surgery until 30 minutes after surgery. This significantly reduced the pain sensation of the subjects during surgery, and the analgesic effect could continue to be maintained after surgery, improving the experience.
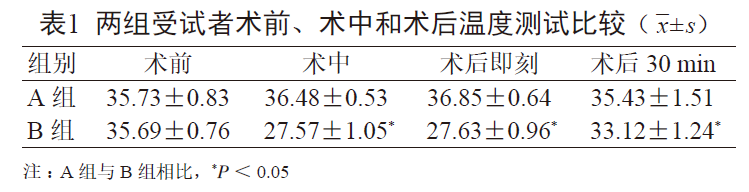
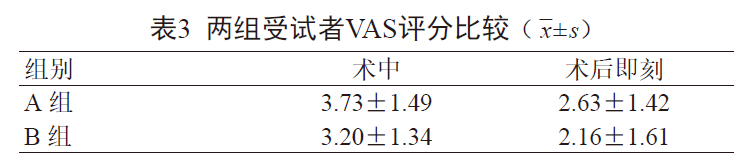
(3) The application of cold air in injection therapy
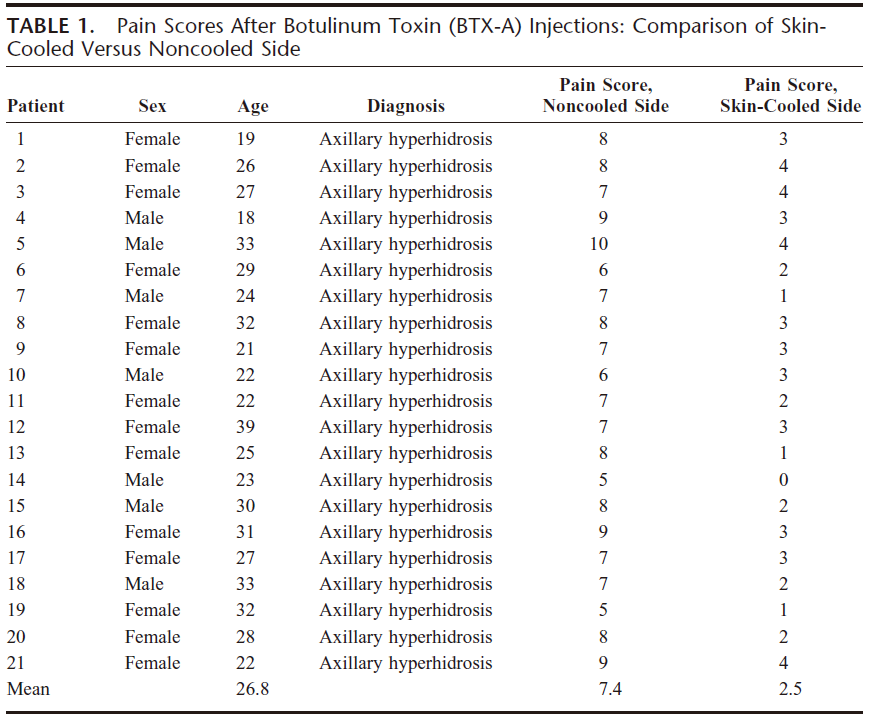
Another application of cold air epidermal cooling in dermatological treatment is to be used in conjunction with injection to reduce pain. Falk G. Bechara et al. [8] and Firas Al Qarqaz et al. [9] conducted experiments on the use of cold air and reached similar conclusions. Cooling with cold air for 1 minute before a single injection of botulinum toxin can reduce the pain score from 7.4 points to 2.5 points, reducing 66.2% of the pain sensation. This greatly reduces the discomfort of patients during injection and improves their tolerance.
5、 Summary: After cold air acts on the epidermis, it can quickly reduce the conduction velocity of nerve cells, constrict blood vessels, decrease vascular permeability, and reduce the release of inflammatory factors; Thereby reducing the surface temperature of the skin, relieving pain during skin treatment, alleviating adverse reactions such as erythema, purpura, and blisters caused by treatment, and shortening the postoperative recovery period. Therefore, cold air epidermal cooling has the characteristics of fast, efficient, non-contact, safe and economical, and is a safe and effective auxiliary solution in dermatology phototherapy and injection processes.
reference:
[1]Guillot X, Tordi N, Mourot L, et al. Cryotherapy in inflammatory rheumatic diseases: a systematic review[J]. Expert review of clinical immunology, 2014, 10(2): 281-294.
[2]Algafly A A, George K P. The effect of cryotherapy on nerve conduction velocity, pain threshold and pain tolerance[J]. British journal of sports medicine, 2007, 41(6): 365-369.
[3]Sari E, Sandikci M M, Bakar B, et al. Estimated beginning time of local anesthesia effectiveness in forced cold air application: A preliminary study[J]. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy, 2016, 18(1): 22-24.
[4]Raulin C, Greve B, Hammes S. Cold air in laser therapy: first experiences with a new cooling system[J]. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine: The Official Journal of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, 2000, 27(5): 404-410.
[5]Greve B, Hammes S, Raulin C. The effect of cold air cooling on 585 nm pulsed dye laser treatment of port‐wine stains[J]. Dermatologic surgery, 2001, 27(7): 633-636.
[6]Hammes S , Raulin C .Evaluation of different temperatures in cold air cooling with pulsed-dye laser treatment of facial telangiectasia[J].lasers in surgery & medicine, 2005, 36(2):136-140.
[7]Zhou Chenxi, Qin Xiaolei, Li Kai, etc Observation of the Safety and Efficacy of Cold Air Coolers in Pain Relief during 1064/532nm Picosecond Dot Matrix Laser Therapy [J] Journal of Practical Dermatology,2023,16(03):150-152+163.
[8]Bechara F G, Sand M, Altmeyer P, et al. Skin cooling for botulinum toxin A injection in patients with focal axillary hyperhidrosis: a prospective, randomized, controlled study[J]. Annals of plastic surgery, 2007, 58(3): 299-302.
[9]Al‐Qarqaz F, Al‐Aboosi M, Al‐shiyab D, et al. Using cold air for reducing needle‐injection pain[J]. International journal of dermatology, 2012, 51(7): 848-852.
Copyright © Suzhou Foremed Legend Technology Co., Ltd.