Share:


The demand for non-invasive beauty technology in the field of skin beauty is increasing day by day, and intense pulsed light (IPL) technology is currently one of the most widely used and popular non-invasive beauty technologies. In order to standardize the use of IPL technology, the Dermatology Society of the Chinese Medical Association (CDA) Skin Laser and Therapy Sub Professional Committee (DLSC) organized some experts to explore the treatment parameters, indications, contraindications, and safety protection of IPL application, and reached a relatively consistent expert opinion, hoping to provide guidance for medical workers.
1、 Working principle
IPL is a type of strong light emitted in a pulsed manner, belonging to non laser light sources, with multi-color, incoherent, and non parallel characteristics. Its light source is an inert gas (usually xenon) flash lamp, and the emitted strong light is condensed and preliminarily filtered, resulting in an IPL wavelength generally between 400 and 1200 nm. Based on the patient's condition, select the appropriate wavelength range. For example, melanin has low absorption of long wavelength light, so longer wavelength filters are selected for patients with darker skin; You can also choose different pulse modes, such as single pulse, double pulse, or triple pulse; The pulse width can also be adjusted within a certain range (from milliseconds to tens of milliseconds), with a commonly used pulse width of 3-5 ms; Pulse delay can cool the skin between two pulses and prevent adverse reactions. The main related factor is the pigment density of the epidermis. The darker the skin color, the longer the time it takes for the epidermis to dissipate heat, usually 20~35 ms. In addition, the energy emitted by traditional strong pulse technology is a decreasing wedge-shaped wave. In order to achieve the therapeutic effect of the last two pulses, the energy of the first pulse needs to be increased, which may cause skin damage. However, the currently used optimized pulse technology (OPT) has a cylindrical light wave emission, with the same energy for each pulse, increasing the safety of treatment. Traditional IPL mostly has adjustable energy levels, and current devices have achieved multi parameter adjustment, which can better target patients with different skin colors and provide personalized treatment in cases where there are differences in skin color, thickness, and depth. IPL can have various cosmetic and therapeutic effects. The following describes the clinical applications of IPL in facial rejuvenation, pigmentary lesions, hair removal, and treatment of vascular diseases.
2、 Facial rejuvenation
(1) The mechanism of facial rejuvenation is mainly reflected in the following aspects.
1. Effects on skin collagen:IPL can enhance the proliferation activity of fibroblasts, thereby increasing the production of new collagen and improving skin appearance. IPL can promote the transcription of type I and III procollagen mRNA in fibroblasts and enhance the synthesis of procollagen. Transforming growth factor β 1 (TGF-β 1) is a major regulatory factor in the biosynthesis of extracellular matrix (ECM) in skin cells. After IPL irradiation, the expression levels of TGF β receptor II, signal transduction molecule Smad4 protein and mRNA in cultured human fibroblasts increased, while the expression levels of Smad7 protein and mRNA decreased. This indicates that IPL irradiation can enhance the activity of TGF β/Smads signaling pathway, stimulate the synthesis and secretion of collagen fibers in skin fibroblasts.
2. Effects on elastic fibers and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs):IPL can promote the renewal and synthesis of elastic fibers, which helps improve skin texture and sagging. MMP can promote the degradation of collagen and other extracellular matrix. Research has confirmed that IPL irradiation can alter the expression of MMP, which has certain benefits for youthfulness.
(2) Facial rejuvenation and photoaging treatment parameters:
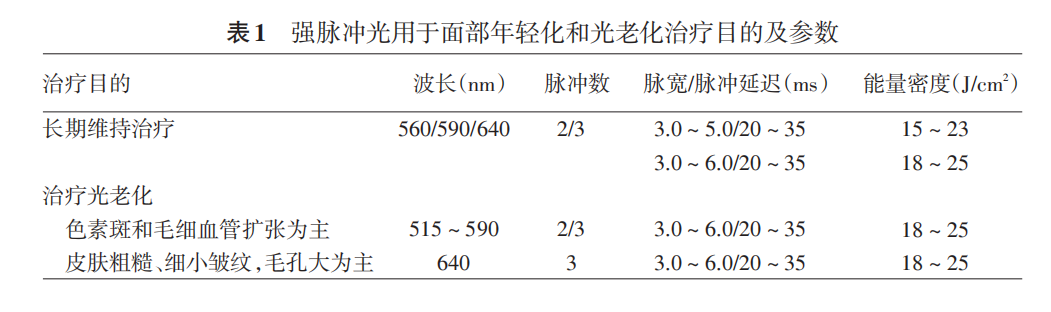
1. Long term treatment:Long term treatment with IPL can effectively promote pigment metabolism, promote skin metabolism, and activate skin repair mechanisms, promoting the proliferation and rearrangement of collagen fibers and elastic fibers. After multiple gentle treatments, it has shown significant effects in improving skin tone and texture (smoothness, delicacy, etc.), as well as enhancing skin elasticity; It has a certain effect on improving fine wrinkles and enlarged pores, but its effect on improving skin laxity is relatively weak. Usually, 2-3 sessions of IPL treatment are needed to achieve ideal results. To achieve better therapeutic effects, a course of treatment (at least 5 sessions) is required. Parameter selection: For darker skin tones, choose smaller energy, longer pulse width, and multiple pulses, while for lighter skin tones, the opposite is true. Reduce energy appropriately in the forehead, temporal region, and lower eyelid area, and increase energy appropriately in the nose; Long term treatment should not affect normal life after surgery. Endpoint reaction: The patient should feel warm. Table 1 lists common indications and parameters for reference.
2. Photoaging treatment:IPL has an ideal therapeutic effect on superficial uneven pigmentation changes in skin texture and pigmentary lesions such as sunspots, seborrheic keratosis, dullness, and pigmentation abnormalities in photoaging treatment; Reliable therapeutic effect on superficial capillary dilation in the face; At the same time, it also improves slight sagging, fine wrinkles, enlarged pores, and glossiness of the skin. In addition to IPL, the treatment of photoaging also requires a comprehensive treatment plan, such as oral or topical antioxidants, pro pigmentation drugs, proper moisturizing and sun protection, a good environment and lifestyle, etc. Parameter selection: If the treatment of pigmented and vascular skin lesions is the main focus, shorter wavelength filters (515~590 nm) can be selected; When treating pigmentary diseases, choose short pulse width; When treating vascular diseases, the pulse width is adjusted according to the diameter of the blood vessel. Short pulse width is used for fine blood vessels, and long pulse width is used for coarse blood vessels; If improving skin quality, fine wrinkles, etc. is the main focus, it is advisable to choose longer wavelength filters (640 nm) and long pulse widths. Treatment endpoint response: When treating pigmentary disorders, the endpoint is when the pigmentation becomes more prominent and there is slight edema around the pigmentation; When treating mild superficial telangiectasia, the endpoint is the fading, blurriness, temporary disappearance, or light gray color of the blood vessels; To treat lesions with changes in the structure of the dermis, the patient should feel warm. See Table 1.
3、 IPL treatment for pigmented lesions
(1) Principle:
In the wavelength range of 280~1300 nm, the wavelength is proportional to the penetration depth, so epidermal pigments absorb short wave light (<755 nm) better, while deeper melanin requires longer wave light (>694 nm, especially 1064 nm). At the same time, with appropriate pulse width, it can act on the pigment target structure. The diameter of melanosomes is 0.5-1 μ m, and the thermal relaxation time (s) of the target structure is generally equal to the square of the target diameter (mm). Therefore, it can be concluded that the thermal relaxation time of melanosomes is between 250 ns and 1 μ s, and the theoretically selected pulse width should be in the nanosecond range (10-100 ns). However, the pulse width of IPL is in the millisecond range, so some scholars believe that when IPL is used to treat pigmentary lesions, its target structure should be cells containing pigments or a certain pigment region. When light is absorbed by melanosomes, it is converted into heat energy, which diffuses to the surrounding area and stimulates rapid differentiation of epidermal cells. Melanosomes also move up and fall off with keratinocytes.
(2) Parameter selection:
Suitable for IPL treatment mainly for pigmented diseases of the epidermis and superficial dermis, such as freckles, sunspots, and other pigmented diseases. For diseases such as coffee spots, melasma, and pigmentation, partial improvement can be achieved. For melanosis, it can be used as one of the means of improvement, but the efficacy is uncertain.
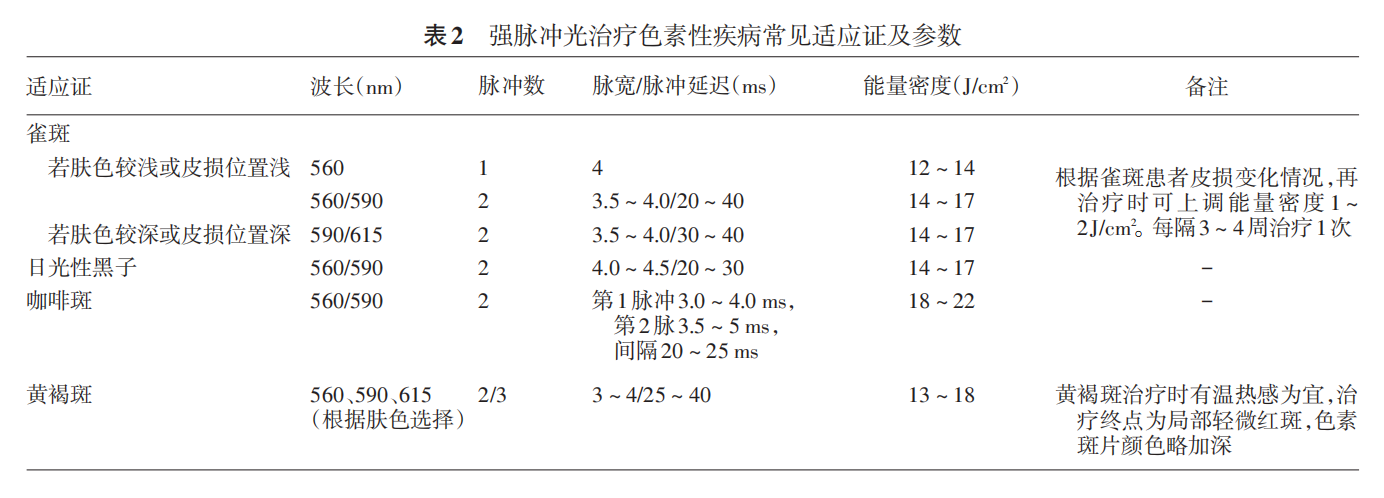
The treatment effect for freckles and sunspots is relatively ideal, but it generally requires multiple (3 times) treatments and cannot prevent recurrence. The skin is whiter, the rash color is darker, the boundary is clear, and compared with normal skin, patients without concomitant melasma have better therapeutic effects. Patients with pale skin lesions, dark skin tone, and combined melasma have poor therapeutic effects. IPL has a significant therapeutic effect on some coffee spots, but the probability of recurrence is high, and when the energy is high, blisters are easily generated in the affected area. Patients with darker rash color and irregular edges have better results. IPL treatment for melasma is mainly used as an adjuvant therapy to accelerate the disappearance of the rash, but it cannot prevent recurrence and requires long-term maintenance treatment. Patients with light skin color, stable rash, and more obvious melasma have a more significant effect. When treating patients with dark skin melasma (skin type Fitzpatrick IV-V), there is a risk of postoperative complications such as pigmentation. Treatment parameters: The key to setting should be based on the patient's skin color, sensitivity, and tolerance. For patients with fair skin tone, lighter skin lesions, and better tolerance, it is necessary to appropriately narrow the pulse width, shorten the interval time, and increase energy density in order to achieve satisfactory clinical results. On the contrary, for those with darker skin tone or darker pigmentation spots, it is necessary to extend the pulse width and interval time accordingly to improve safety and reduce adverse reactions. The recommended parameters for IPL treatment of several pigmentary diseases are shown in Table 2.
4、 Hair removal
IPL hair removal has definite efficacy and mild adverse reactions, and is still one of the main methods of hair removal to this day. Its indications are hirsutism and excessive hair.
(1) Principle:
When used for hair removal, although the target of IPL is melanin, its true biological target is stem cells located in the prominence of hair follicles. So, to achieve hair removal, melanin needs to absorb light energy, which is then converted into heat energy to destroy hair follicles and hair follicle stem cells. For hair follicle melanin, the maximum wavelength absorption range is 590~900 nm, and epidermal melanin can also compete to absorb this wavelength of light. However, within a certain range, the longer the wavelength of light, the stronger its penetration ability, and the less melanin is absorbed by the epidermis. Therefore, IPL hair removal is suitable for patients with light skin color, and should be used with caution for those with dark skin color.
(2) Parameter selection:
1. Wavelength selection:In order to achieve hair removal effect, the growth area and hair follicles of the hair must be precisely illuminated by light. The spectrum with a wavelength of 600~1100 nm can penetrate to the depth where hair follicles are located and be well absorbed by melanin, making it an ideal wavelength range for laser hair removal.
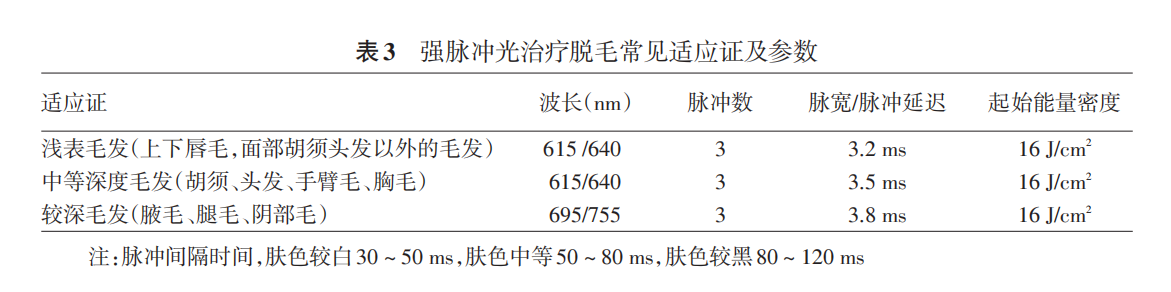
2. Pulse width selection:The ideal pulse width should be between the thermal relaxation time of the epidermis and the thermal relaxation time of the hair follicle, with the thermal relaxation time of the epidermis being 3-10 ms; The diameter of hair follicles can reach 200~300 μ m, and the thermal relaxation time can reach 40~100 ms. The ideal pulse width range for IPL hair removal is 10~100 ms or even longer. For people with dark skin, in order to avoid adverse reactions caused by excessive absorption of light energy by the epidermis, it is advisable to increase the pulse width appropriately. With the protection of a good epidermal cooling system, the pulse width can even be increased to several hundred milliseconds. The recommended treatment parameters for IPL hair removal based on different types of hair are shown in Table 3.
3. Treatment course:Due to the fact that hair follicle stem cells only proliferate during the hair growth phase, a maximum of 15% to 30% of hair can achieve permanent shedding in a single treatment. Within one month after hair removal treatment, most of the hair is in the resting phase, after which the hair follicles gradually recover and enter the growth phase. Therefore, the treatment interval is 4-6 weeks, and the best time for further treatment is when the hair grows 2-3 mm. Generally speaking, the thicker the hair, the darker the color, and the fewer treatments it receives; The finer and softer the hair, the lighter the color, and there are relatively more treatments. The more treatments, the better the therapeutic effect.
5、 Vascular diseases
Vascular lesions suitable for IPL include superficial vascular lesions such as telangiectasia, facial and neck follicular erythema and blackening, and red wine stains. Redness and blackening of hair follicles in the face and neck can often be alleviated in the short term, but skin lesions are prone to recurrence after a few months. Patients should be informed that this is a temporary improvement measure. IPL has limited effectiveness in treating vascular diseases such as red wine stains, often focusing on fading. The effect varies in different parts, with the neck showing the best effect and possibly achieving significant improvement. Strawberry shaped hemangiomas often protrude above the skin, and strong pulsed light energy is relatively easy to reach the superficial blood vessels inside the hemangioma. Treatment can reduce blood vessels, alleviate the tendency of skin thickening and turning red, and slow down or even improve the development of the hemangioma in the short term. Due to the difficulty of IPL energy penetrating deep into the skin, the energy mainly accumulates in the epidermis, which can easily cause adverse reactions such as pigmentation changes. Patients with dark skin are at a higher risk
(1) Principle:
When IPL is used to treat vascular lesions, the target is hemoglobin. Hemoglobin has three absorption peaks at 418, 542, and 577 nm, respectively. Although the maximum absorption peak is at a wavelength of 418 nm
The wavelength penetration is poor and can be competitively absorbed by epidermal pigments, so the wavelength close to the last two peaks should be selected for the treatment of vascular lesions. When light is absorbed by hemoglobin and converted into heat energy, endothelial cells undergo thermal coagulation, which closes blood vessels and achieves therapeutic effects. It should be emphasized that only when the distal (far from the skin surface) blood vessels are also closed, can the blood vessels be permanently closed, otherwise blood vessel recanalization is prone to occur. Therefore, IPL is more effective for superficial vascular lesions.
(2) Parameter selection:
The more short wavelengths are retained, the shallower the effect, the stronger the effect on pigments, but the greater the impact on the epidermis, and the higher the possibility of causing pigment deposition; The more long wavelengths are retained, the more biased the effect is towards the dermis layer, resulting in less possibility of pigmentation, but the corresponding effect on pigment treatment is reduced, which may be more suitable for vascular and skin rejuvenation treatment. Around 577 nm is a wavelength that is well absorbed by blood vessels, but considering the issue of wavelength absorption, 560 nm filters are often used in clinical practice for better performance. IPL is mainly targeted at blood vessels with relatively small diameters, so the heating time does not need to be very long. For patients with dark skin, the pulse width of IPL is relatively wide and can be set as small as possible within a safe range, which is beneficial for improving treatment intensity. Treatment endpoint: Reasonable parameter settings often require only one scan to complete the treatment. If there is limited local reaction after surgery, treatment can be strengthened as appropriate. There is another type of narrow spectrum IPL with an emission spectrum of 500-600 nm, which has a stronger effect on vascular skin lesions than traditional IPL due to its better coverage of the absorption peak of hemoglobin at around 530 nm. However, melanin also has strong absorption in this spectral range, so patients with darker skin should be cautious when using it. Such patients are prone to epidermal damage, leading to pigmentation or hypopigmentation. The typical application parameters are a pulse width of 10~12ms and an energy density of 8~15J/cm ² (commonly 10~12J/cm ²). During treatment, the cooling mode (50%, 75%, or 100%) can be selected according to the situation. Treatment endpoint: The vascular skin lesions become lighter, temporarily disappear, or appear light gray. The swelling reaction after treatment is more pronounced than traditional intense pulsed light.
6、 Acne and rosacea
1. Indications for acne: ① Red imprints and pigmentation spots after the disappearance of inflammatory acne lesions, with significant therapeutic effects; ② Moderate acne mainly characterized by papules and pustules. Acne treatment requires a complete sequential treatment plan, and IPL treatment alone is not preferred. It can be combined with medication treatment. In clinical practice, photodynamic therapy can be performed alone or in combination with aminolevulinic acid (ALA) as a light source. Adjust parameters based on the characteristics of the patient's inflammatory skin lesions, skin color, and tolerance level. Select 560 nm/590 nm/640 nm filters, dual pulse or triple pulse, pulse width 3.0~4.5 ms, pulse delay time 20~40ms, energy density 15~18 J/cm ². Single treatment does not overlap, with mild redness of the skin lesions as the endpoint of treatment. 4-6 treatments are considered as one course of treatment, with an interval of 3-4 weeks between each treatment. Some treatment devices are equipped with 420 nm filters.
2. Indications for rosacea:① Erythema telangiectasia type, with definite therapeutic effect, requiring multiple treatments and may have recurrence; ② Papular pustular type, may present with worsening reactive symptoms, treatment should be cautious. The parameter selection before treatment is the same as for acne. Adjust parameters based on the degree of capillary dilation, skin color, and tolerance of the patient. If the energy is low, treat with mild skin heat and flushing as the endpoint
7、 Contraindications
1. Absolute contraindications:Photosensitive skin and photosensitive related diseases; The skin lesions in the treatment area are precancerous lesions or malignant tumors; Infection in the treatment area; Treating open wounds in the treatment area; Patients with excessively high treatment expectations
2. Relative contraindications:Patients taking oral retinoids should use with caution; Individuals with a history of sun exposure within the past 2 weeks who are unable to protect themselves from the sun after surgery; Pregnancy or lactation period; Individuals with scar constitution; Patients with weakened immunity or currently taking glucocorticoids or immunosuppressants; Individuals with coagulation dysfunction; Individuals with mental illnesses or disorders who are unable to cooperate with treatment; Individuals with other serious systemic diseases Consensus of clinical application experts
Copyright © Suzhou Foremed Legend Technology Co., Ltd.